Hydroponics and aquaponics are popular farming methods. Both promise efficient plant growth.
But how do they really compare? Understanding the differences can help you choose the best system for your needs. Hydroponics uses nutrient-rich water to grow plants. Aquaponics combines fish farming with plant cultivation. Each method offers unique benefits and challenges.
Comparing them helps you decide which fits your environment and resources. This blog explores these two systems. It highlights their distinct features and potential advantages. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a curious beginner, this guide aims to provide clear insights. Dive in to discover which system aligns with your goals.
Credit: gogreenaquaponics.com
Introduction To Modern Farming
Modern farming is transforming how we grow our food. With the world’s population increasing, traditional farming methods are struggling to keep up. Enter hydroponics and aquaponics, two innovative techniques that promise sustainability and efficiency.
These methods are not just for large-scale farmers. Even if you have a small space, you can start your own garden. Think of the joy in harvesting fresh produce from your living room or backyard.
As someone who once struggled with growing a simple tomato plant, discovering hydroponics felt like finding a treasure. No more worrying about soil quality or pests. You simply focus on nurturing your plants.
Rise Of Sustainable Methods
Why are sustainable methods gaining popularity? For starters, they reduce water usage. With hydroponics, you use up to 90% less water compared to traditional farming. Aquaponics takes it a step further by recycling water through fish tanks.
These techniques also offer space-saving solutions. Whether you’re living in an apartment or have limited backyard space, you can grow a garden vertically. It feels empowering to turn small spaces into productive farms.
One weekend, I decided to set up a small hydroponic system in my kitchen. Within weeks, I had fresh basil and lettuce. It was a game-changer, proving that sustainable farming is accessible to everyone.
Why Compare Hydroponics And Aquaponics
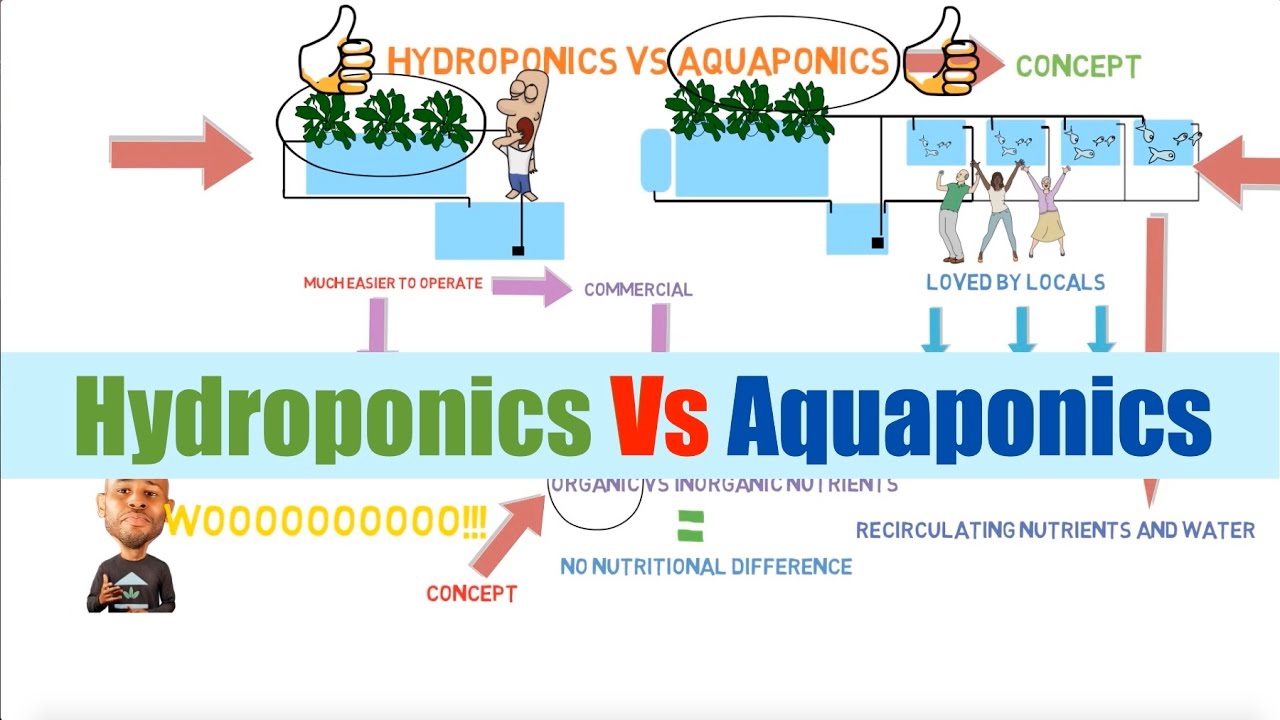
It’s crucial to understand the differences between hydroponics and aquaponics. Hydroponics relies solely on nutrient solutions to feed plants. Aquaponics integrates fish tanks, creating a symbiotic environment where fish waste provides nutrients.
Knowing which system suits your needs can save time and resources. Hydroponics might be ideal if you prefer a straightforward setup. Aquaponics could be your choice if you enjoy maintaining a fish tank alongside your plants.
Imagine setting up a small aquaponics system. You’re not just growing plants but also nurturing fish. This dual purpose can be both rewarding and challenging, offering a unique farming experience.
So, which method appeals to you? Are you ready to dive into the world of modern farming and create your own green oasis?

Credit: www.atlanticwatergardens.com
Basics Of Hydroponics
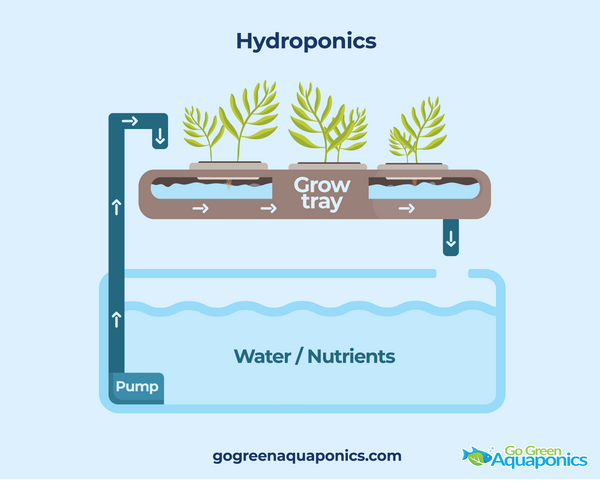
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil. It uses a nutrient-rich water solution to support plant growth. This technique is popular for its efficiency and control over plant nutrition. Hydroponics allows for faster plant growth and higher yields in small spaces. Let’s explore how it works and the key components needed.
How Hydroponics Works
In hydroponics, plants grow in a water-based environment. The roots are submerged in a nutrient solution. This solution provides essential minerals and nutrients. Plants absorb these directly from the water. This method eliminates the need for soil. Nutrient delivery is precise, leading to optimal growth. Lighting and temperature are controlled for best results.
Key Components And Equipment
A hydroponic system requires several components. First, a reservoir holds the nutrient solution. This solution is pumped to the plants. A growing medium supports the roots. Common mediums include clay pellets and rock wool. Grow lights provide necessary light for photosynthesis. Pumps and timers regulate nutrient delivery. Monitoring equipment checks pH and nutrient levels. Proper ventilation ensures air circulation. Each component plays a vital role in plant health.
Principles Of Aquaponics
Aquaponics is a blend of aquaculture and hydroponics. It creates a balanced ecosystem. This system relies on the natural relationship between fish and plants. Fish produce waste, which becomes nutrients for plants. In turn, plants purify the water for fish. The result is a sustainable, efficient growing environment. This method conserves water and space. It also eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers.
Understanding Aquaponics Systems
An aquaponics system has three main components: the fish tank, the grow bed, and the pump. The fish tank holds the fish. The grow bed is where plants grow. The pump circulates water between them. Water flows from the fish tank to the grow bed. Here, plants absorb nutrients from fish waste. Clean water returns to the fish tank. This cycle repeats continuously.
Fish And Plant Symbiosis
The fish and plants in aquaponics have a symbiotic relationship. Fish produce waste that is rich in ammonia. Bacteria convert ammonia into nitrates, which are nutrients for plants. Plants absorb these nitrates, cleaning the water. This purified water goes back to the fish tank. Both fish and plants thrive in this environment.
Comparative Analysis
In the world of soilless farming, hydroponics and aquaponics stand out. Both systems offer sustainable ways to grow plants indoors or in limited spaces. But what are the key differences? A comparative analysis reveals their strengths and weaknesses. Explore their efficiency, yield, and resource use.
Efficiency And Yield Differences
Hydroponics often delivers faster plant growth. It uses nutrient-rich water, directly feeding plant roots. This leads to bigger yields in a shorter time. Plants in hydroponics can grow 30-50% faster than in soil. Aquaponics, on the other hand, integrates fish into the system. The fish waste provides nutrients for the plants. This creates a balanced ecosystem. Yield in aquaponics might be slower initially. But it offers fish as an added harvest. Over time, aquaponics can become highly productive.
Resource Utilization
Hydroponics requires precise nutrient solutions. These need to be monitored regularly. Water usage is efficient, but nutrients must be replenished often. Aquaponics combines fish farming with plant growth. This reduces the need for external fertilizers. Fish produce waste that nourishes the plants. Water recirculates, minimizing waste. Both systems save water compared to traditional farming. Yet, aquaponics supports a dual crop system. This can mean more resource use upfront. Balancing fish and plant needs is crucial.
Environmental Impact
As you venture into the world of modern gardening, understanding the environmental impact of hydroponics and aquaponics becomes crucial. Both systems promise sustainable agriculture, but how do they really measure up? Let’s dive into the specifics.
Sustainability Factors
Hydroponics uses water efficiently, which is a major plus. You can grow plants without soil, using less space and avoiding soil erosion. However, it requires synthetic nutrients, which might not be as eco-friendly as you’d like.
On the other hand, aquaponics combines fish farming with plant cultivation. This system creates a symbiotic relationship where fish waste provides nutrients for plants. It’s organic and natural, but maintaining the balance can be tricky.
Have you considered how much energy each system uses? Hydroponics can consume more due to pumps and lights. Aquaponics might be more energy-friendly if you use solar power and gravity-fed systems.
Waste Management
Hydroponics generates minimal waste, as excess water can be recycled. But what happens to the old nutrient solution? Disposing of it responsibly is key to reducing environmental harm.
In aquaponics, fish waste is your friend. It’s transformed into plant food, closing the waste loop effectively. But what if you don’t manage the fish properly? Overfeeding can lead to water quality issues.
Do you have a strategy for handling plant waste? Composting can be a great solution, turning old stems and leaves into valuable soil for traditional gardening.
Both systems have their unique challenges and benefits. How do you balance efficiency with environmental responsibility? Your choices can make a significant difference in the impact your garden has on the planet.
Credit: www.youtube.com
Economic Considerations
Choosing between hydroponics and aquaponics involves understanding their economic impacts. Both systems offer sustainable ways to grow plants. Yet, they differ in setup costs and market potential. Considering these factors helps make an informed choice. Below, explore crucial economic aspects of each system.
Cost Of Setup And Maintenance
Hydroponics often requires a lower initial investment. It uses fewer components and simpler technology. Basic setups need containers, nutrients, and a water system. Maintenance involves regular nutrient solution changes. This system suits those on a budget.
Aquaponics demands a higher initial cost. It involves integrating fish tanks, bio-filters, and pumps. The system’s complexity increases maintenance needs. Fish care adds to ongoing expenses. Yet, it offers dual yields: plants and fish. This appeals to some despite higher costs.
Market Potential
Hydroponics has an expanding market potential. Urban farming and local produce demand drive interest. Many consumers prefer pesticide-free options. Hydroponics meets this need efficiently.
Aquaponics taps into niche markets. It offers organic produce and fresh fish. Restaurants and local markets value these products. The dual output can increase income streams. This makes aquaponics attractive for certain businesses.
Health And Safety Aspects
Health and safety in hydroponics and aquaponics matter greatly. They influence the quality of food produced. Both systems have unique benefits and concerns. Understanding these aspects helps in making informed choices.
Nutrient Quality
Hydroponics uses mineral nutrient solutions. These solutions are carefully controlled. They ensure plants get essential nutrients. This control leads to consistent produce quality. Aquaponics relies on fish waste for nutrients. Fish waste creates a natural nutrient cycle. The cycle enriches plant growth. It can result in nutrient-rich produce. Both methods aim for high nutrient quality.
Disease Control
Disease control is crucial for healthy plants. Hydroponics uses sterile environments. These environments reduce disease risks. Regular monitoring helps in early detection. Aquaponics involves living organisms. This complexity can introduce diseases. Managing fish health is important. Proper care minimizes disease impact. Both systems require diligent monitoring.
Future Of Indoor Farming
The future of indoor farming looks promising. With limited land and water, innovative methods are necessary. Two leading methods are hydroponics and aquaponics. Both offer sustainable solutions. They use fewer resources and improve crop yield. As technology advances, these systems become more efficient. Let’s explore their future in the farming industry.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements enhance both hydroponics and aquaponics. Sensors monitor plant growth. Automated systems control nutrients and lighting. AI helps optimize resource use. These technologies reduce labor and increase productivity. They make indoor farming more accessible. Engineers design better systems every year. This progress makes these methods more popular.
Global Adoption Trends
Indoor farming is gaining popularity worldwide. Urban areas face land scarcity. Hydroponics and aquaponics offer solutions. Many countries invest in these technologies. Governments see them as sustainable options. They help reduce food imports. Both systems are ideal for urban farming. Their adoption grows as more people learn about them.
Hydroponics and aquaponics appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. These systems use less water. They produce fresh food locally. This reduces carbon footprints. As awareness grows, so does global adoption. Indoor farming could become the norm.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Aquaponics Better Than Hydroponics?
Aquaponics can be more sustainable than hydroponics due to its natural ecosystem. It combines fish farming with plant cultivation. Hydroponics offers faster growth and requires less space. The choice depends on your priorities, such as sustainability or efficiency. Both methods have unique benefits and challenges.
What Are 5 Disadvantages Of Aquaponics?
Aquaponics systems can be expensive to set up. They require constant monitoring and maintenance. Technical knowledge is essential for troubleshooting. Limited crop variety can be grown. Power outages can disrupt system balance.
What Are 3 Disadvantages Of Hydroponics?
Hydroponics can be costly due to equipment and energy needs. It requires constant monitoring and technical expertise. Disease can spread quickly in water systems, affecting plant health.
Can Fish Live In Hydroponic Water?
Fish can live in hydroponic systems if properly managed. Aquaponics combines fish and plant growth, benefiting both. Ensure water quality and balance nutrients for healthy fish and plants. Regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial for success in hydroponic environments.
Conclusion
Choosing between hydroponics and aquaponics depends on your goals. Hydroponics suits those wanting fast, efficient plant growth. It uses nutrient solutions without fish. Aquaponics integrates fish and plants, offering a natural cycle. Fish provide nutrients for plants, creating harmony. Both systems save water and space.
Hydroponics is simpler, while aquaponics has more components. Consider space, budget, and maintenance needs. Evaluate your resources and desired outcomes. Start small, learn, and grow your system gradually. Each method offers unique benefits. Find what works best for you and enjoy the process of growing your garden.






